How to Relieve and Prevent Patellar Tendinopathy
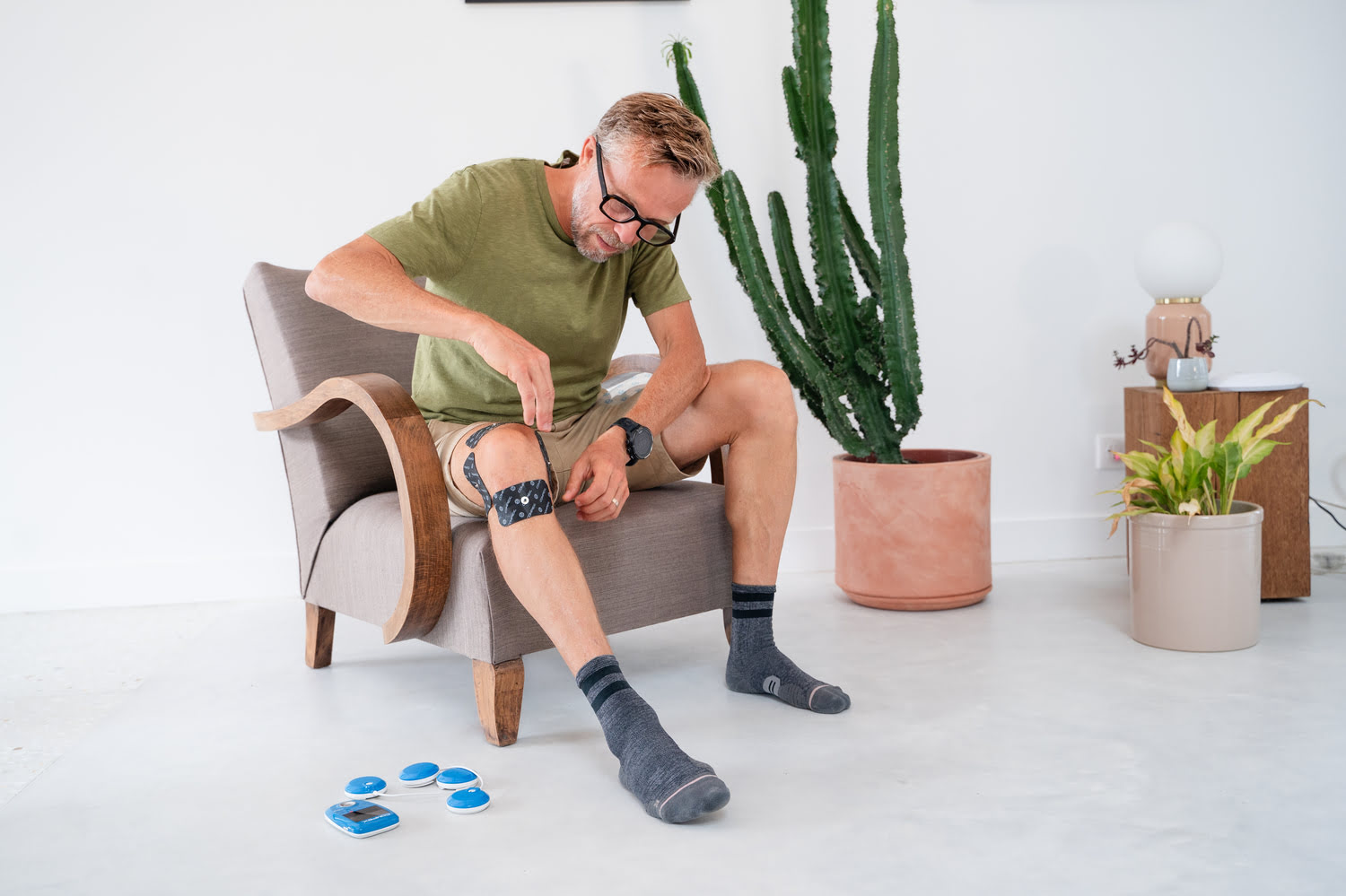

Patellar tendinopathy is a condition that affects the tendon that connects the patella to the tibia bone. This tendon is called the patellar tendon or quadricipital tendon.
When you bend or extend your leg, the patellar tendon allows your muscles to move the patella and generate the force needed to make these movements.
Patellar tendinopathy occurs when this tendon becomes irritated, inflamed or damaged. This can occur as a result of a number of factors, such as repetitive movements involving the knees, overuse, trauma or anatomical problems.
Symptoms of patellar tendinopathy can vary from person to person, but common signs include:
- Pain in the front of the knee, around or under the kneecap.
- Pain during physical activity, such as running, jumping or simply bending the knee.
- Tenderness or pain when you touch or press the affected area.
- Stiffness or a feeling of weakness in the knee.
If you suspect that you have patellar tendinopathy, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or physiotherapist. They will be able to assess your symptoms, make a precise diagnosis and recommend a suitable treatment plan.
What causes Patellar Tendinopathy?
Patellar tendinopathy can be caused by a number of factors. Here are a few things that may contribute to its onset:
- Overuse: Frequent repetition of movements that put strain on the knees. Jumping, striding or excessive bending of the knee can lead to patellar tendinopathy.
- Poor Technique: Poor movement technique during physical activities can put excessive pressure on the patellar tendon, leading to irritation or inflammation. This can happen if the thigh muscles are not strong enough to properly support the patella.
- Anatomical Factors: Certain anatomical factors can increase the risk of developing patellar tendinopathy. For example, a patella that is not correctly aligned or an anatomical malformation can create additional stress on the patellar tendon.
- Muscle Weakness: Muscle imbalance, particularly weakness in the quadriceps, can put excessive pressure on the patellar tendon. If the muscles surrounding the kneecap are not strong enough to absorb the forces during movement, the tendon can become overloaded.
- Trauma: Direct trauma, such as a fall on the knees or a violent blow, can damage the patellar tendon and cause tendinopathy.
- General Health Factors: Certain medical conditions, such as arthritis, diabetes or obesity, can increase the risk of developing patellar tendinopathy. Additionally, poor blood circulation or a reduction in the body's ability to heal can influence tendon health.
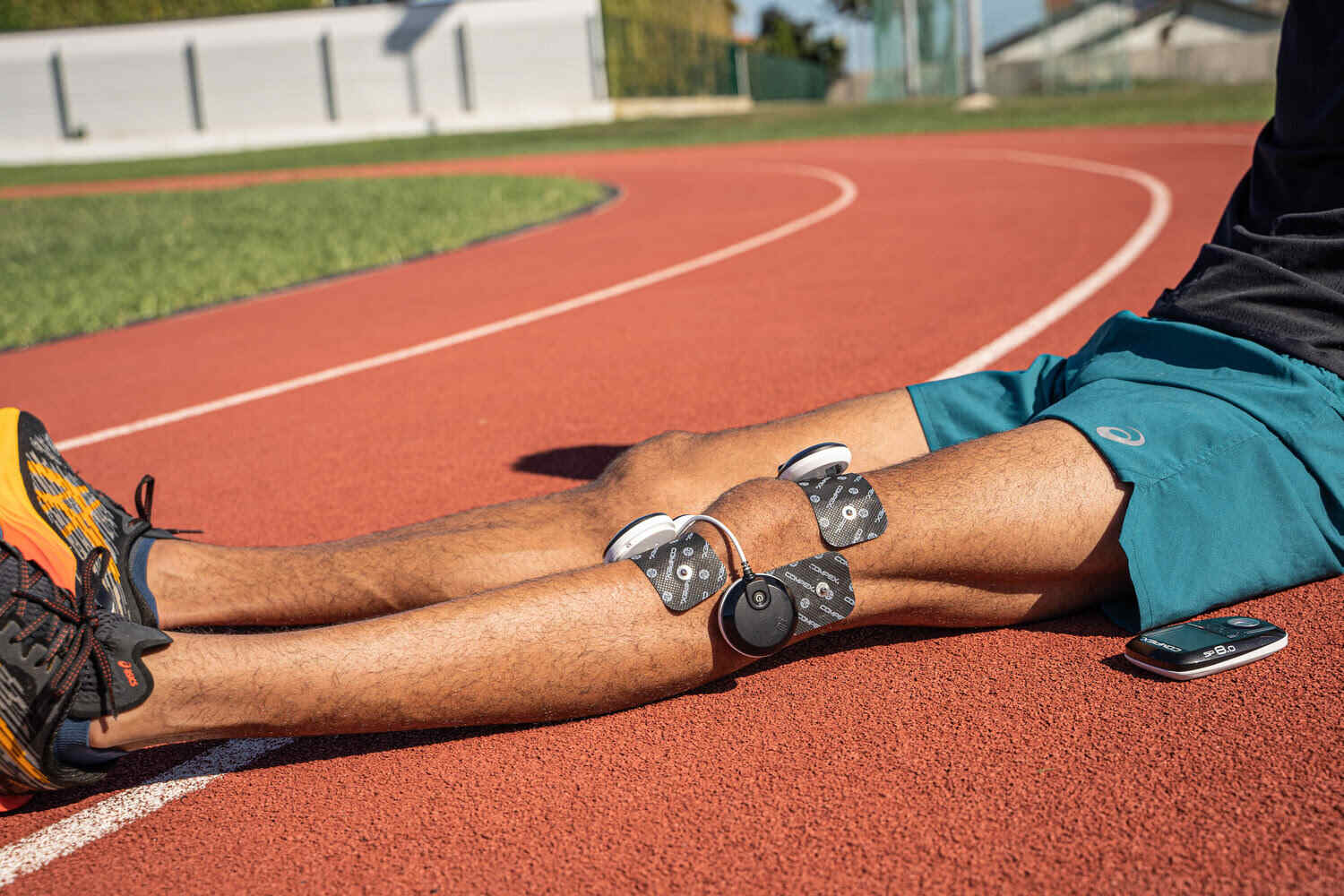

Sports that can Risk Causing Patellar Tendinopathy
As far as overuse is concerned, the following sports can be at risk of causing patellar tendinopathy, due to the repetitive or excessive stress exerted on the patellar tendon:
- Running: Regular and prolonged running, particularly on hard surfaces, can put intense strain on the patellar tendon.
- Jumping sports: Sports that involve frequent jumping, such as basketball, volleyball, high jumping or pole vaulting, put significant pressure on the patellar tendon.
- Ball sports: Sports such as football, tennis, handball, cricket and rugby can require fast movements, sudden changes of direction and jumping actions, which can bring on patellar tendinopathy.
- Cycling: Although cycling is generally considered to be a low-impact activity for the knees, inadequate ergonomic adjustments or excessive intensity can lead to excessive strain on the patellar tendon.
- Combat sports: Combat sports such as judo, boxing or karate can involve rapid movements and heavy loads on the knees, which can increase the risk of patellar tendinopathy.
Treatment of Patellar Tendinopathy
Treatment for patellar tendinopathy can include rest, modification of physical activities, application of ice, use of anti-inflammatory medication, use of TENS and also specific muscle strengthening exercises with or without electrostimulation.
Wireless Device
Wired Device
Recovery Period for Patellar Tendinopathy
The recommended rest period for patellar tendinopathy may vary depending on the severity of the injury and the specific recommendations of your healthcare professional. In general, rest is important to allow the tendon to heal and regenerate. However, prolonged rest can also lead to muscle weakness and loss of fitness.
The use of electrostimulation during the period of enforced rest may be considered to help maintain or minimise the loss of muscle mass. You can use electrostimulation passively stimulate muscles and induce muscle contractions without any active physical effort.
If you have an electrostimulator, we recommend that you start by using our muscle conditioning programs on your quads. Don't hesitate to download the free Compex Coach app for more details. However, if you are planning to use electrostimulation during your enforced rest, it is advisable to consult a health professional or physiotherapist who can assess your specific condition and offer you suitable advice.
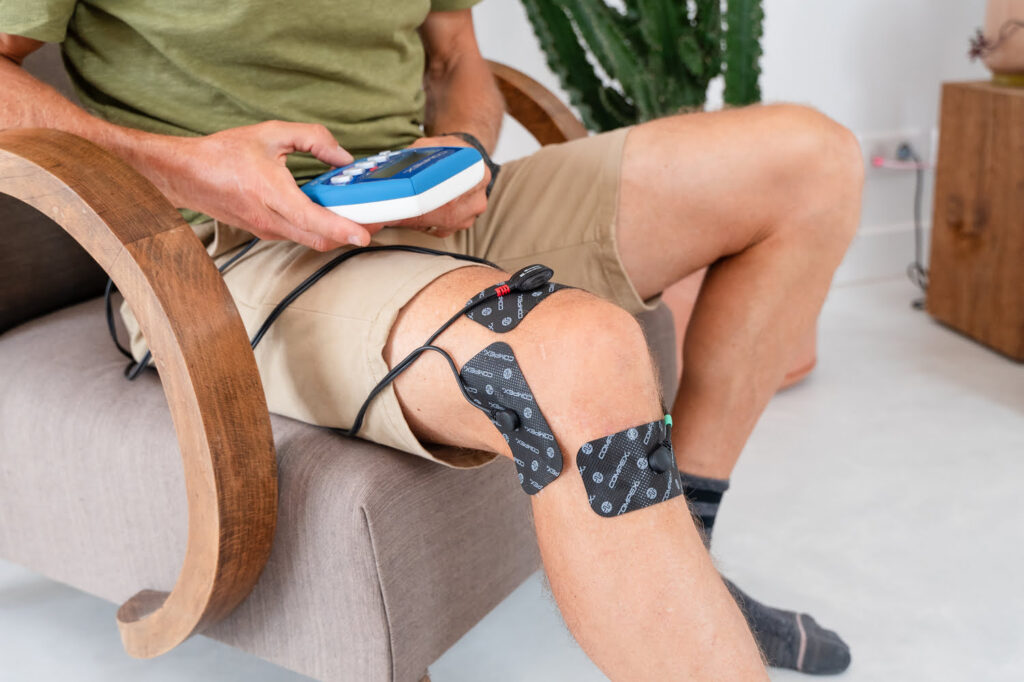

Reintroduction of Physical Activity
Returning to physical activity gradually is usually encouraged after a rest period. This may involve specific muscle strengthening exercises, stretching, or low-impact activities for the knees, under the supervision of a healthcare professional or physiotherapist. The aim is to strengthen the muscles around the knee to stabilise the patella and promote proper healing.
It is important to note that each case of patellar tendinopathy is unique, and rest and recovery times may vary from person to person.
Relieving the Pain of Patellar Tendinopathy
TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) using a muscle stimulator or other TENS device is a treatment mode used to relieve pain. It involves applying electrodes to the skin, close to the painful area, which deliver light electrical impulses.
In the case of patellar tendinopathy, the use of TENS may be help individuals as a method of pain management. However, note that TENS does not directly treat the underlying cause of patellar tendinopathy.
TENS can help to alleviate pain by partially blocking the transmission of pain signals to the brain and releasing endorphins, which are natural pain-reducers. This may offer temporary relief, but it is important to understand that TENS does not cure patellar tendinopathy itself.
It is recommended that you consult a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or physiotherapist. They can provide an accurate diagnosis of patellar tendinopathy and advice on appropriate treatments. They will be able to recommend a comprehensive approach to pain management. This may include TENS as well as other treatments, such as therapeutic exercise, stretching, or other treatments.
Preventing a Recurrance of Patellar Tendinopathy
It is important to follow the advice and recommendations of your healthcare professional to promote healing and prevent recurrence. Progressive rehabilitation, muscle strengthening and avoiding activities that worsen symptoms can help relieve patellar tendinopathy.
There are a number of steps you can take to prevent patellar tendinopathy or reduce the risk of it occurring. Here are a few tips:
- Strengthen Leg Muscles: It is essential to strengthen your thigh muscles, particularly the quadriceps, to support and stabilise the patella. Exercises such as squats, lunges, leg extensions and pelvic muscle strengthening exercises can help.
- Increase Training Intensity Gradually: Avoid sudden increases in the intensity or length of your training. Gradual increases allow your muscles and tendons to adapt.
- Warm Up and Stretch: Warm up properly before any physical activity to prepare your muscles and tendons for exertion. Dynamic stretching can also be useful to improve the flexibility of the muscles involved in knee movement.
- Use Proper Technique: Learn proper movement techniques and use proper form during physical activities, especially those that put strain on the knees. Poor movement technique can increase stress on the patellar tendon.
- Wear Appropriate Footwear: Use appropriate shoes for your physical activities. They need to offer good support, cushioning and stability to reduce the impact on the knees.
- Listen to your Body: Give your body time to recover between training sessions and intense physical activities. If you feel pain or discomfort in your knee, take a break and consult a health professional if necessary.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on joints. This includes the knees, which can help prevent injuries and tendon disorders.

Proven Effectiveness
Backed by clinical studies proving their effectiveness, Compex stimulators also belong to the category of Class II medical devices. They also meet the requirements of the European Medical Standard 93/42 EEC.
Compex - Always with you
We're on the side of athletes, amateurs and also ordinary people. From the search for better performance to post injury recovery, from post fatigue massage to pain treatment. At Compex, we have just one goal: people's well being.
To choose the one that's right for you, take a look at our buying guide.
Read our experts' advice on the official blog, catch the latest Compex news by subscribing to our newsletter. You can also watch our videos on the YouTube channel and follow us on Facebook and Instagram to stay up to date.