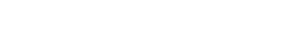Effective Pain Treatment with Electrostimulation (EMS)

Not all pains are the same, and depending on their origin, the complex issues involved can be very different in nature, as can the treatment of pain. Everyone has experienced pain and can relate to it. Whether it's headaches or pain resulting from hitting your fingers with a hammer - in both cases, it hurts (a lot), but the body's reactions to each pain are very different. The same goes for the most common pains experienced by athletes, and depending on the nature of the injury, different methods of electrostimulation for pain relief need to be considered.
The pain relief category is one of the most-used on Compex devices. This type of program is involved in the treatment of certain pathologies, always in addition to the work of healthcare professionals such as physiotherapists.
In this article, we won't discuss rehabilitation - this element is up to your physiotherapist to implement it with a protocol to follow. Based on this protocol, you can then use your Compex device to help provide effective pain treatment.
We can generally identify two types of pain that can be addressed with Compex programs:
- Muscular pains
- Non-muscular pains
Looking at the list of pain relief programs, they can be differentiated into two main groups:
- TENS-type programs
- And EMS-type programs (electrical muscle stimulation)
| EMS-type programs | TENS-type programs |
| Reduce Muscle Tension | Pain Management TENS |
| Muscle Pain | Tendinitis |
| Neck Pain | Epicondilitis |
| Back Pain | |
| Lumbago | |
| Heavy Legs | |
| Cramp Prevention |
What's the difference between TENS and EMS?
TENS-type programs are completely different from all other programs you can find in a muscle stimulator. They are the only ones that don't seek to stimulate muscle fibers since they stimulate nerve fibers instead.
Thus, TENS-type programs produce a tingling sensation.
EMS-type programs, on the other hand, stimulate muscle fibers and should therefore produce muscle contractions.
Now that you understand this difference well, we will explain how to use these programs correctly so that you can make the most of them.
Pain Treatment programs: TENS, Tendinitis, Epicondylitis
The most important point to emphasise is that pain is a symptom. Something is not working well in our body, but pain doesn't allow you to identify the source. This should lead you directly to consult your doctor so that they can evaluate the cause of this pain and the treatment required.
But what's clear is that this pain limits your movements, and consequently, it diminishes your quality of life. You can then take advantage of the tools at your disposal to improve this quality of life. And this is where TENS-type programs come in as an effective form of pain treatment. These programs do not cure the pathology causing the pain, but they alleviate this discomfort and thus improve your well-being. That's why these programs are an excellent complement to the treatment that a physiotherapist can perform.

When to use a TENS-type program for pain treatment
You can use TENS-type programs as a form of pain treatment for any pain or discomfort. This will mainly involve joint and tendon pain, as these are structures that you cannot stimulate with electrostimulation. You can also use it to relieve other types of localized pain, such as menstrual cramps. These programs can also work in the treatment of pain such as burns.
Electrode placement for effective pain treatment
Place the electrodes directly on the painful area, whether there is muscle tissue in the area or not. If there is muscle tissue, it doesn't matter the direction of the muscle fibers, as these programs do not seek to stimulate muscle fibers. In case of a burn, frame the area to start the pain treatment, rather than covering it.
The most common electrode placements for this type of program are as follows:
1st. You place one electrode just above the painful point, which will be the + pole, and another electrode next to it, at a maximum distance of about 5cm. It doesn't matter in which direction you place the second electrode.
2nd. Position the painful point between two electrodes. It doesn't matter whether you connect to the + and - poles. As we said in the first case, you will set the maximum distance between the electrodes to about 5cm. If the area is larger, you can use more channels.
Body position
The body position should be as relaxed as possible when looking for treatment of pain. Avoid generating tension in the muscle structures involved in the painful area. For example, if you have knee pain, when applying TENS - avoid generating tension in the knee. Keep the leg stretched and relaxed, without muscular tension in the quadriceps.
Intensity of use
The right intensity is the one that gives you a simple tingling sensation. No muscular response should appear during pain treatment, either in the form of muscle twitching or contraction, as this response can be counterproductive and therefore undesirable. When you reach the tingling sensation, you do not increase the intensity anymore. When you no longer feel the tingling sensation, then you can increase the intensity again. This is very personal and depends on each person and each area of the body being treated. This action is normal, as your body gradually gets used to this sensation.
Usage time
TENS-type programs, like all programs in a muscle stimulator, have a predetermined duration. If you wish to repeat a program to elongate your pain treatment, you can do so without any problem or contraindication, but we recommend leaving 10 to 15 minutes between each session.
Another important point: the more you use this program, the shorter the analgesic effect lasts. Therefore, we recommend using it when necessary and not overusing it to avoid reducing its benefits.
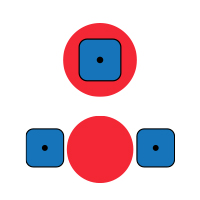
When to use Muscle Tightness and Lumbago programs
The programs target and provide pain treatment the same problem: recent muscle tightness.
Lumbago is a program dedicated to the lumbar region, due to its parameters, and the Reduce Muscle Tension program is a more generic program that can be used anywhere. But the goal of these two programs is exactly the same: to fight against recent muscle tightness and give effective pain treatment. Here are some examples of recent tightness: calf tightness when resuming running or contracture of the anterior right quadriceps when kicking a ball or tightness in the neck region from sleeping in a bad position, etc. All these cases or similar cases are to be treated with the Reduce Muscle Tension program.
Electrode placement

As we can see, the electrode placement is exactly the same as in TENS-type programs. The big difference is to consider the direction in which the electrodes are placed, as they should follow the direction of the muscle fibers. So:
1st: place one electrode just above the painful area, which will be the positive pole. Then place another above or below, always in the direction of the muscle fibers, where we will connect the negative pole.
2nd: You put the painful area between two electrodes. In this case, the positive and negative poles do not matter. As we said in the first case, place the electrodes in the direction of the muscle fibers.
If in doubt about placement on a muscle, we recommend using the placements used for specific muscle training. You can also use the free Compex Coach app or head to our website to see all electrode placements.
Body position
Position yourself in a completely relaxation position.
Intensity of use
In this case, we are talking about EMS-type programs. In these programs, muscle stimulation occurs as your muscle fibers' respond by twitching. From there, it is very important to determine the appropriate intensity, as the wrong intensity can be counterproductive.
The correct intensity for this type of program should be one that causes powerful but comfortable muscle twitches. That is, a very gentle muscle twitch will be ineffective and will not produce the desired effect. However, excessive intensity is even worse, as this excess intensity will cause discomfort in the muscle, which, to protect itself from this aggression, will contract, which could lead to worsening the pathology instead of improving it.
Comfort and strength are very subjective notions. The MI functions provide us with objectivity and that allows us to improve its effectiveness. The MI Range (FIT 5.0, SP 4.0, and SP 6.0 models) and Mi Autorange (SP 8.0 model) functions offer you the guarantee that the intensity you are using is adequate and, therefore, the most effective when using these programs. Find out more information on the MI-technology here.
Usage time
You can use it as many times as necessary, without any contraindication in this regard.
Using Muscle Pain, Back Pain and Neck Pain Programs for effective pain treatment
These three programs target the same problem, a chronic contracture.
We consider a sprain or heavy muscle tightness to be chronic when you have been experiencing it for more than three days. During the first three days, you can use the Reduce Muscle Tension program, and from the fourth day, if the tightness has not eased and seems to be settling in, you start using the Muscle Pain program. If the pain is located in the lumbar region: Back Pain, in the cervical region: Neck Pain. The difference between the programs is that Back Pain offers parameters more suitable for this area of the body, and the same is true for Neck Pain. The Muscle Pain program is a generic one that can be used on any area of the body.
The difference between these programs
The difference between the Reduce Muscle Tension and Muscle Pain programs lies in the program parameters, and more specifically in the frequencies. Compare the two programs and you will see that the Reduce Muscle Tension program produces very slow muscle twitches (one muscle twitch per second), while the Muscle Pain program is faster (five muscle twitches per second). The reason for this difference in frequency is that the effects sought by the two programs are different.
If with the Reduce Muscle Tension program, the only thing we seek is to relax the contracted muscles, in the case of tightness that has become chronic, we need to be more effective to obtain results. Muscle tension is a contraction of a group of muscle fibers that persists without rest. Muscle contraction compresses blood vessels in the affected muscle, so that contracted muscle fibers receive less blood, and therefore fewer nutrients and oxygen. This means that over hours and days, the tension that was small at the beginning expands, increasing the size of the painful area.
Thus, the Muscle Pain program, in addition to providing muscle relaxation, produces two other effects:
- Increased blood flow: It manages to open the blood vessels that were compressed and thus provide nutrients and oxygen to these fibers that were no longer nourished.
- Increased endorphin secretion: Endorphins are the famous "feel-good hormones" or "pleasure hormones," as they are commonly called. You will feel better when a greater secretion of these hormones occurs in your body, and muscle pains are reduced.
Body position, use intensity and usage time
The body position and intensity of use suitable for these programs, as well as the recommended usage times, are exactly the same as those we explained for the Reduce Muscle Tension program previously.
Remember that most of the time, tightness occurs to protect a vital structure. For example, tension of the lumbar or cervical muscles generally seems to protect the spine, limiting its movements. Therefore, if chronic tensions occur regularly, it is essential to consult a physiotherapist so that they can establish a care and exercise protocol to attack the root of the problem and thus prevent it from reoccurring.
Finally, we reiterate that what we have explained in this article does not replace the treatment of a physiotherapist but that Compex programs are rather a complement. Therefore, if your pains persist, we recommend consulting a healthcare professional so that they can make a diagnosis.
Proven Effectiveness
Backed by clinical studies proving their effectiveness, Compex stimulators also belong to the category of Class II medical devices. They also meet the needs of the European Medical Standard 93/42 EEC.
Compex - Always with you
We're on the side of athletes, amateurs and ordinary people. From the search for improved performance to post injury recovery, from post fatigue massage to pain treatment. At Compex, we have just one goal: people's well being.
Choose the one that's right for you, by taking a look at our buying guide.
Read our experts' advice on the official blog, catch the latest news, product releases and promotions by subscribing to our newsletter, and watch our videos on the YouTube channel and follow us on Facebook and Instagram to stay up to date.