How to Prevent Lumbago Back Pain and Avoid a Recurrence

Are you struggling with back pain? Don't worry, you're not alone. It seems to be the ailment of the century. Lumbago is also known as back pain or lower back pain. It's a common condition that can cause intense pain and greatly limit mobility. This pain is mainly felt in the lumbar vertebrae, located in the lower back. In this blog, we will explore the various aspects of lumbago and discuss the causes, risk factors, prevention methods, and solutions to relieve your back pain.
What is Lumbago?
Lumbago is generally associated with physiological mechanisms involving the spine, muscles, and joints. The spine plays a crucial role in maintaining posture and body stability. When there is a change in the structure or function of the spine, it can lead to lower back pain.
The back muscles, especially the paravertebral muscles, are also essential in maintaining the stability of the spine. Muscle weakness or imbalance in these back muscles can increase the risk of lumbago.
Additionally, the joints of the spine, including intervertebral joints and facet joints, can be susceptible to wear and tear and/or inflammation. This can contribute to the development of lumbago.
The Different Types of Lumbago
Acute lumbago refers to sudden and intense lower back pain. It usually occurs following an injury, sudden movement, or excessive effort. This type of lumbago is often short-lived and can be relieved with rest and proper care.
Chronic lumbago, on the other hand, is characterised by persistent lower back pain lasting beyond 12 weeks. It can be caused by factors such as structural problems in the spine, chronic muscle tension, or underlying medical conditions.
Another common type of lumbago is related to a herniated disc. In this case, the intervertebral disc, acting as a cushion between the vertebrae, can move or tear, causing pressure on nerves and resulting in lower back pain.
Causes and Risk Factors
Injuries are one of the most common causes of lumbago. Poor posture when lifting heavy objects, sudden movement, or direct trauma - these factors can lead to excessive strain on the muscles and ligaments of the lumbar region, causing acute pain.
Abrupt and repetitive movements, especially during intense physical activities or poorly executed exercises, can also overly stress the muscles of the lower back and lead to lumbago.
Obesity and being overweight are also significant risk factors. Excess weight puts additional pressure on the spine and lumbar muscles, leading to pain and posture problems.
Sedentary lifestyle and lack of regular physical exercise weaken the back muscles, making the spine less stable and more prone to injuries and strains.
Lastly, postural problems, such as poor sitting position or imbalanced posture, can create muscle imbalances and excessive pressure on the spine, contributing to the development of lumbago.
Who Is at Risk of Lumbago?
Age is a significant risk factor, as the structures of the spine tend to degrade over time. Intervertebral discs become less flexible and less capable of absorbing shocks, increasing the risk of lumbago.
Individuals engaged in intense physical work or heavy loads have an increased risk of developing lumbago. Excessive physical stress on the spine can also lead to muscle tension and injuries.
Stress can also play a role in lumbago development. Chronic stress can cause increased muscle tension, especially in the lumbar region, raising the risk of lower back pain.
Family history of lumbago can increase the likelihood of developing this condition. Certain spine related conditions, like herniated discs, may have a genetic component, predisposing some individuals to back problems, including lumbago.
Understanding these risk factors enables us to provide tailored preventive advice for each individual, emphasising risk reduction and promoting back health.
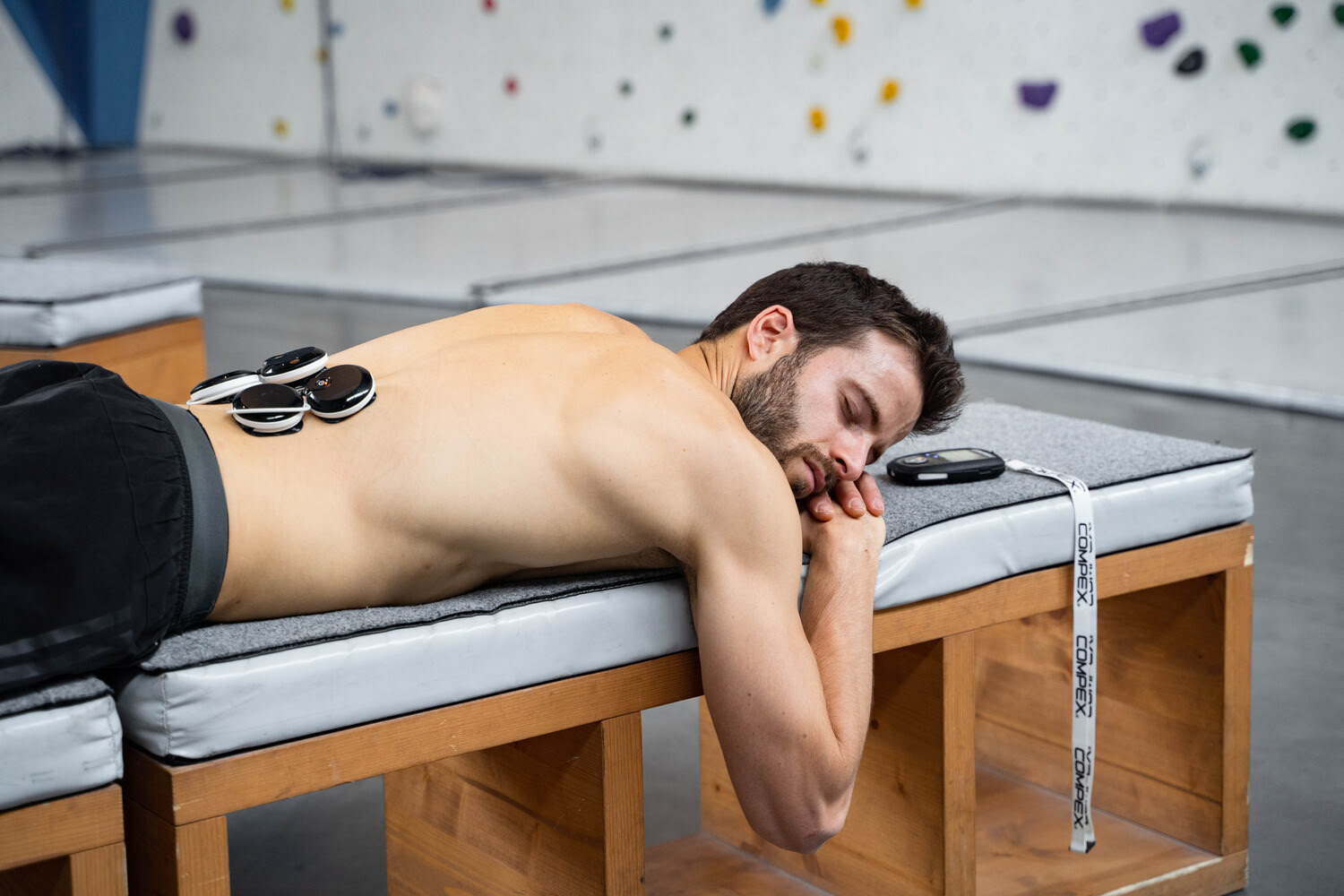

3 Tips to Prevent and Manage Lumbago
Tip #1 – Posture and Muscle Strengthening
Poor posture can put excessive pressure on the spine, increasing the risk of lumbago. It's essential to maintain good posture when sitting, standing, and lifting heavy objects. Ensure proper alignment of your back, keep your shoulders relaxed, and support your spine.
Strong and balanced back muscles provide support and stability to the spine, reducing the risk of lumbago. Incorporate specific back muscle strengthening exercises into your workout routine, such as back extensions, hyperextensions, or core exercises.
Regular physical activity helps to maintain the flexibility and strength of back muscles, preventing back problems. Try activities like swimming, yoga, walking, or cycling. These will help promote back movement and muscle strength.
Avoid sudden movements and excessive twisting of the back, especially when handling heavy objects. Use proper lifting and carrying techniques. Also, avoid abrupt movements and repetitive gestures that overly stress the spine.
Tip #2 – Natural Relief Methods
- Hot and/or Cold Compression: Hot and cold compresses can provide immediate relief for lower back pain. Compex offers the ColdForm Back wrap which can help on this front. Applying a hot compress can relax tense muscles and improve blood circulation, while a cold compress can reduce inflammation and numb the painful area. It's recommended to alternate between the two to find what works best for you.
- Specific stretches: Targeted stretches can help relieve tension and improve the flexibility of back muscles. Gentle and controlled stretching exercises, such as back, hip, and leg stretches, can help reduce pressure on the spine and reduce lower back pain.
- Massages: Massages can be helpful for relieving lumbago. They reduce muscle tension and improve blood circulation in the lumbar region. Gentle massage of the lower back, either by a professional or using a massage device, can help relax muscles and relieve pain.
- Relaxation Techniques: Stress management and relaxation are also crucial for lumbago relief. Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or tai chi can help reduce muscle tension, improve posture, and promote overall relaxation.
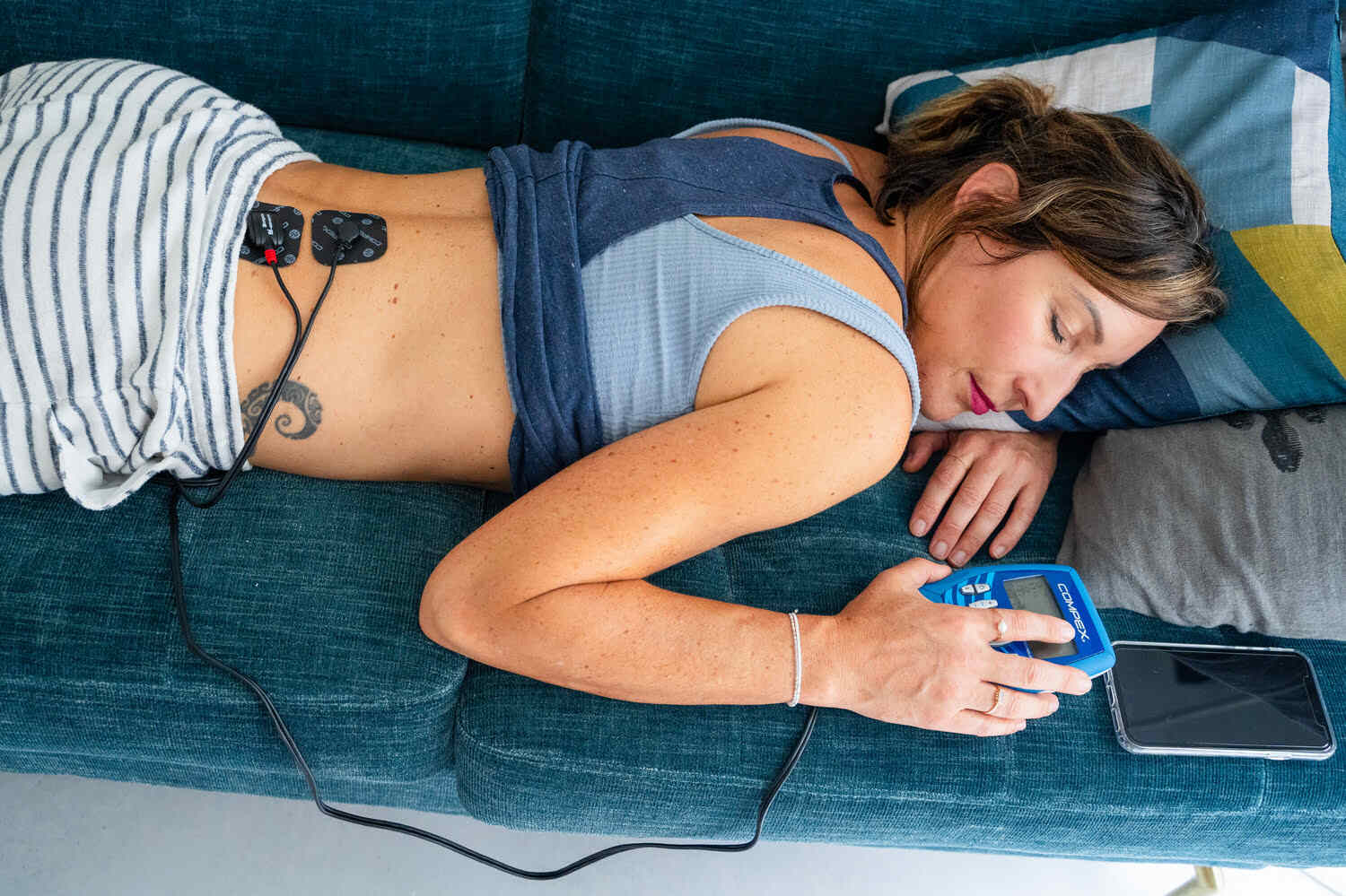
Tip #3 – Electrostimulation to the Rescue
Electrostimulation devices, such as those offered by the Compex brand, provide an innovative approach to pain management and muscle recovery for back pain.
When pain is present, it often involves persistent contractions or spasms of the lumbar paravertebral muscles. These can be effectively combated and relieved with the Lumbago program (available on our SP 8.0 and FIT 5.0 devices). It directly targets pain by triggering an increase in the body's natural production of endorphins. It also acts on muscle contraction by significantly increasing local blood flow, helping to remove acidic waste in the muscles. For more details, refer to this article: Treating Lower Back Pain with Electrostimulation.
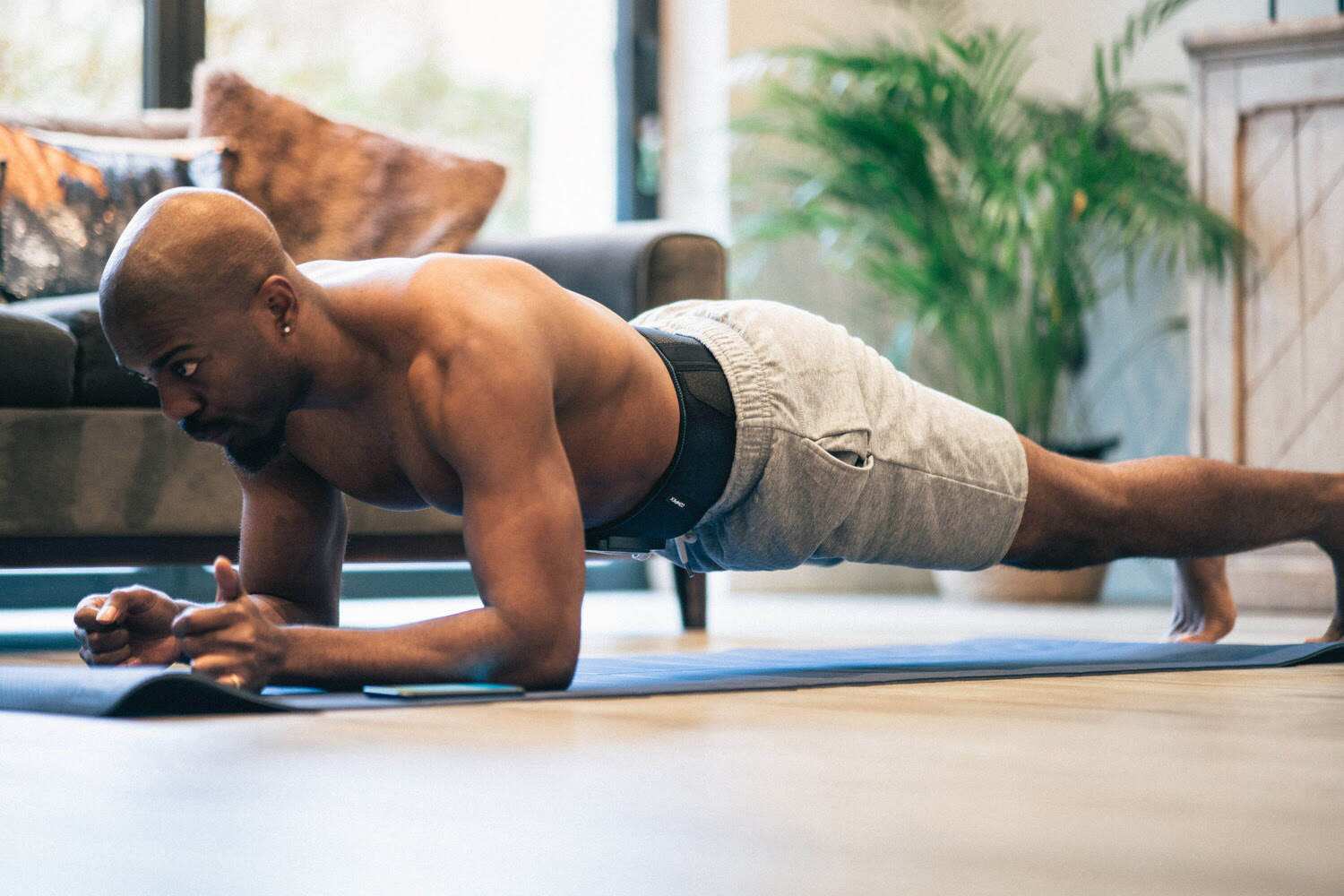
Work on Your Core Strength to Prevent a Recurrence
Core strength training involves strengthening deep abdominal muscles (psoas, iliac, lumbar square, transverse abs, and obliques) and the dorsal muscle chain in static contraction. During static exercise, muscles work without creating movement, without changing length. Abdominal core exercises help lose belly fat and protect intervertebral discs. They also help develop proprioceptive qualities by ensuring overall trunk muscle tone. Like dynamic abdominal muscle exercises, static core muscle training promotes the transmission of vertical impulse forces during strides or jumps.
Electrostimulation is a technique that has demonstrated its effectiveness in this area due to the ability it has to recruit a significant percentage of overall muscle fibers in the target muscles. The quality of stimulation currents, as found in all Compex stimulators, allows for the recruitment of the deepest muscle fibers. This enables all muscles of the abdominal core to work, not just the superficial rectus abdominis muscles. Large obliques, small obliques, and the deep transverse muscle, along with all the lumbar paravertebral muscles, contract powerfully with long duration contractions to develop their ability to perfectly stiffen the lumbar spine for an extended period. More details can be found in this article: Treating Lower Back Pain with Electrostimulation.
The Compex Corebelt devices can also assist you in achieving this goal.

Lumbago: a Conclusion
Lumbago can be a painful and debilitating condition. However, with the right prevention and management measures, it's possible to reduce risks and improve the quality of life. By incorporating practices such as maintaining proper posture, appropriate muscle strengthening, using natural relief techniques, and electrostimulation, it's possible to effectively prevent and relieve lumbago. Consult a healthcare professional for correct diagnosis and advice suited to your situation.
Do not ignore pain. Consult a doctor if the lumbago pain is severe and/or lasts for too long.
Proven Effectiveness
Backed by clinical studies proving their effectiveness, Compex stimulators also belong to the category of Class II medical devices and meet the requirements of the European Medical Standard 93/42 EEC.
Compex - Always with you
We're on the side of athletes, amateurs and also ordinary people. From the search for better performance to post injury recovery, from post fatigue massage to pain treatment. At Compex, we have just one goal: people's well being.
To choose the one that's right for you, take a look at our buying guide.
Read our experts' advice on the official blog, catch the latest Compex news by subscribing to our newsletter. You can also watch our videos on the YouTube channel and follow us on Facebook and Instagram to stay up to date.