Abdominal Contracture: Definition, Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Have you ever experienced intense and persistent abdominal pain, accompanied by unusual muscle stiffness? This could be an abdominal contracture—an urgent signal from your body that requires immediate attention.
Imagine this: you're in great shape, and suddenly, your stomach feels as hard as concrete, with sharp pain. What’s happening? Why does this occur? And most importantly, what should you do?

In this article, we dive into the heart of excessive and potentially serious muscle tension. Get ready to discover:
- What an abdominal contracture really is and why it happens.
- The symptoms to watch out for.
- Effective treatments to relieve your pain and prevent complications.
Whether you’re personally affected or seeking information for someone close, this article may transform how you view this muscle condition.
Ready to uncover the mysteries of abdominal contracture and take control of your well-being? Keep reading, and your body will thank you!
What is an Abdominal Contracture?
An abdominal contracture is an involuntary, prolonged contraction of the abdominal wall muscles. Unlike a simple muscle spasm, a contracture is persistent and often associated with intense pain. Moreover, it frequently signals peritoneal irritation, which indicates inflammation or infection within the abdominal cavity, such as in cases of peritonitis.
Causes of Abdominal Contracture
Several causes may lead to an abdominal contracture, including:
- Peritonitis: Inflammation of the peritoneum, often due to a bacterial infection, is a frequent cause. It can result from the perforation of an abdominal organ, such as the appendix or a gastric ulcer.
- Appendicitis: Inflammation of the appendix can trigger an abdominal contracture, typically felt in the lower right quadrant of the abdomen.
- Abdominal Trauma: A blow or injury to the abdomen may lead to a reflexive muscle contracture to protect internal organs.
- Gastrointestinal Diseases: Inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis may also cause abdominal contractures.
Symptoms of Abdominal Contracture
Symptoms associated with abdominal contractures can include:
- Severe Abdominal Pain: Pain is often sharp and worsens with pressure applied to the abdomen.
- Abdominal Wall Stiffness: The abdomen may feel rigid to the touch, a classic sign of contracture.
- Increased Sensitivity: There can be heightened sensitivity to pressure or touch.
- Other Symptoms: Depending on the underlying cause, additional symptoms like fever, nausea, vomiting, or changes in bowel habits may occur.
Diagnosing Abdominal Contracture
Diagnosing an abdominal contracture involves a thorough clinical examination, often supported by imaging tests and lab analyses. The doctor will palpate the abdomen to assess the presence and location of the contracture. Imaging, such as ultrasound or CT scans, may be used to identify the underlying cause of peritoneal irritation.
Treatment for Abdominal Contracture
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Common approaches include:
- Medical Treatment: In cases of infection, antibiotics may be prescribed. Pain relief and anti-inflammatory medications can help reduce discomfort and inflammation.
- Surgery: If the contracture is caused by a condition requiring surgery, such as appendicitis or organ perforation, an operation may be necessary.
- Recovery: Hydration, nutrition, and rest are key to aiding the body’s recovery.
Prevention and Long-Term Management
Preventing abdominal contractures involves proactively managing underlying health conditions and taking measures to avoid abdominal injuries. Regular medical check-ups and paying attention to early symptoms can help prevent serious complications.
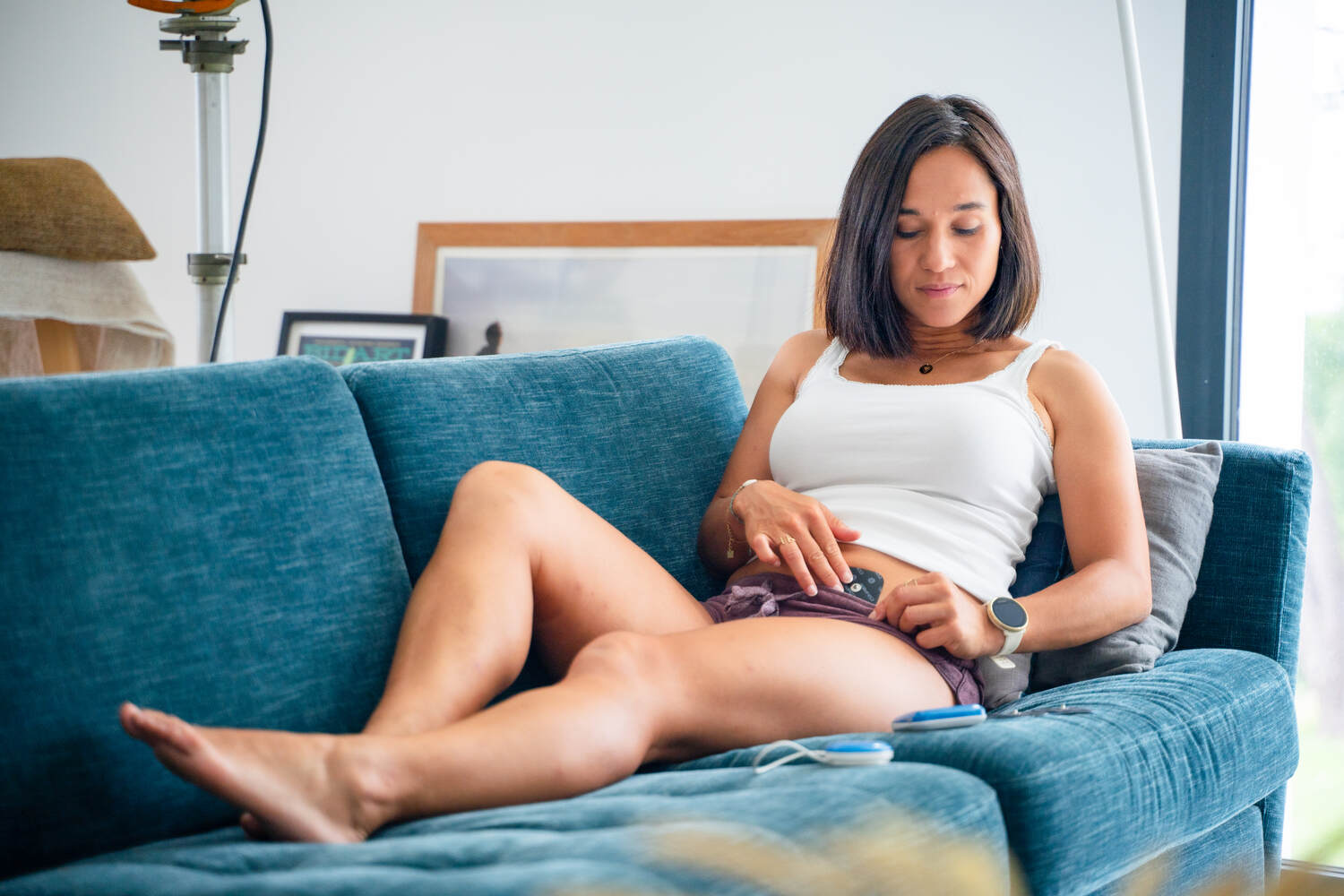
Electro-Stimulation: A Helpful Tool for Abdominal Contractures

Electro-stimulation is becoming more common for treating various muscle conditions, including abdominal contractures. This technique involves applying electrical impulses to the muscles to trigger contractions, which can help relieve pain and improve muscle recovery.
How Does Electro-Stimulation Work?
Electro-stimulation devices send electrical impulses to the motor nerves of muscles via electrodes placed on the skin. These impulses mimic signals from the brain, causing muscle contractions. This approach can be particularly beneficial in reducing muscle contractures and alleviating associated pain. By relaxing tense muscles, it achieves these effects without necessitating physical effort. Consequently, it offers a practical solution for managing muscle tension and discomfort.
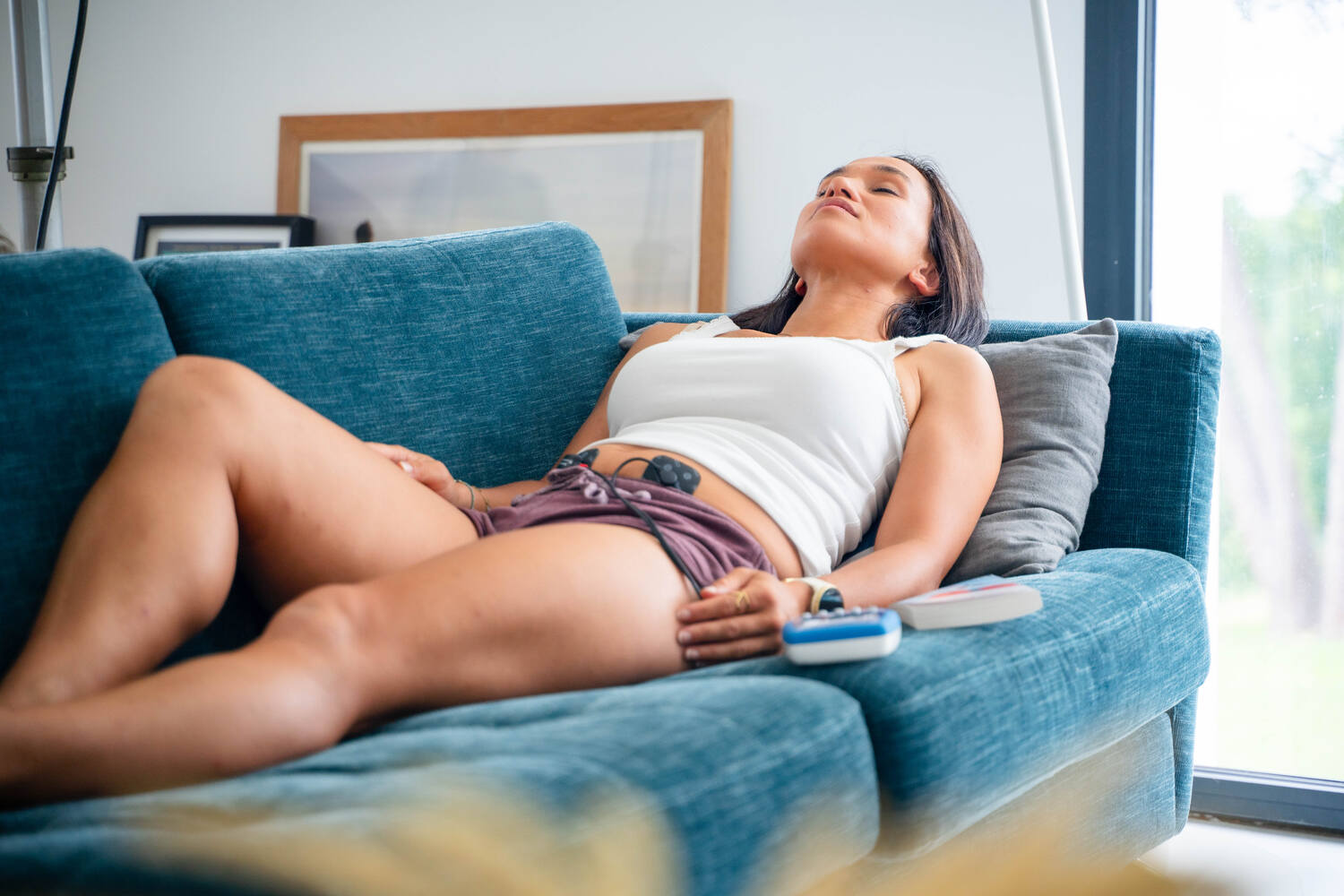
Benefits of Electro-Stimulation for Abdominal Contractures
- Pain Relief: Electro-stimulation can reduce pain perception by stimulating nerve fibres, which is especially useful for abdominal pain.
- Muscle Relaxation: Specific electro-stimulation programmes help relax contracted muscles, reducing stiffness and discomfort.
- Improved Blood Circulation: By enhancing peripheral vascularisation, electro-stimulation promotes better blood flow, which can speed up recovery.
Precautions and Contraindications
Although generally safe, use electro-stimulation with caution. Healthcare providers do not recommend it for individuals with pacemakers, pregnant women, or those with conditions like epilepsy. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional before starting electro-stimulation therapy to ensure it’s suitable for your situation.
Take Action Quickly: Your Guide to Managing Abdominal Contracture
Abdominal contracture is a serious muscle condition that necessitates immediate medical attention. This urgency arises due to its potential link with severe abdominal issues. Consequently, addressing this condition promptly is crucial to prevent further complications. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments is key to effective management.
Electro-stimulation can be a useful tool in managing abdominal contractures, providing a non-invasive way to relieve pain and improve muscle function. It's best to use this therapy under a healthcare provider's guidance to prevent complications and maximise benefits.
Proven Effectiveness
Backed by clinical studies proving their effectiveness, Compex stimulators also belong to the category of Class II medical devices. They also meet the needs of the European Medical Standard 93/42 EEC.
Compex - Always with you
We're on the side of athletes, amateurs and ordinary people, from the search for improved performance to post injury recovery, from post fatigue massage to pain treatment. At Compex, we have just one goal: people's well being.
Choose the one that's right for you, by taking a look at our buying guide.
Read our experts' advice on the official blog, catch the latest news, product releases and promotions by subscribing to our newsletter, and watch our videos on the YouTube channel and follow us on Facebook and Instagram to stay up to date.